Massage Therapy isn’t just for relaxation… though it can be very relaxing.
Massage Therapy causes changes in the body that:
- Trigger the relaxation response
- Boost the immune system
- Reduce muscle tension
- Stimulate of the production of endorphins
- Increase blood and lymph circulation
- Relax and normalize the soft tissue (muscle, connective tissue, tendons, ligaments), which releases nerves and deeper connective tissues
Together, these responses can produce physical and emotional benefits.
What is the relaxation response?
The relaxation response is a state in which your heart and breathing rate slow, your blood pressure goes down, your production of stress hormones decreases, and your muscles relax. The relaxation response also seems to increase the available level of serotonin, which is a chemical in the body that positively affects emotions and thoughts.
This relaxation response can act as a treatment for stress-related illnesses such as hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, anxiety, insomnia, persistent fatigue, sexual dysfunction, digestive disorders, and psychological issues.
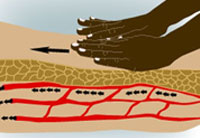
Improved circulation can enhance the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to muscle cells. As cellular health improves, tissues function more efficiently. More efficient functioning leads to the removal of waste products and may increase the absorption of excess fluids and reduce swelling in soft tissues.
Relaxing Tissue
Massage therapy relaxes muscle tissue, which reduces painful contractions and spasms. Massage can also reduce nerve compression. To understand this, consider that when muscles are contracted, they sometimes compress the nerves around them. When these muscles are relaxed, the nerves are no longer compressed, and, in theory, can get proper nutrients and operate more efficiently. The nerves can assume their normal work of transmitting messages to and from the brain, which improves functioning of the muscles and organs.
Touching the skin or applying pressure relaxes muscles, tendons, and ligaments. In addition, while some of the deeper tissues of the body, such as deep spinal musculature, cannot be easily accessed by a massage therapist, the release of more superficial layers of muscles may also affect these deeper layers. This can lead to both superficial and deep tissues finding a better alignment and balance.
Organs can also benefit from massage, as they share neurological pain pathways with muscles, bones, and nerves. When muscles, bones, or nerves are distressed, organs can sometimes reflect distress and dysfunction.
Book your next massage at 613-549-0866